Starting Phase comes to an end.
Before moving to the next phase, answer yourself to these to make sure you can move on to the next phase (Beginner Phase ) .
Questions on the dealt topics faced in the first phase of learning.
Starting phase :
- What are the compilers in C#?
- What is an assembly in C#?
- What is a class library in C# , What is the use of Class library in C#.?
- What is a namespace in C# , name few namespaces used in C#?
- What are the differences between WriteLine() and Write()?
- What are the comments and region in C#? How you define and what are i=the types of comment used.
- Do comments affect your code and what are its uses?
- What are data types in C# , list few of them?
- Type Conversion/ Type Casting in C#?
- What are different types of Operators in C#?
- What are unary operators?
- What are the conditional statement?
- Explain looping, give an example to illustrate the difference between for and while loop in C#?
- Ternary operator syntax in C#.
- Difference between C and C#?
Some sample program to practice;
1.Write a program to print like below ;
Name : Your lovely name
DateOfBirth: 27/01//1993
Address: Singapore
Mobile No: 897xxxxxxxxxxx
Email: [email protected]
2.Write a program to print the maximum of 3 numbers i.e 9 , 7 , 3 without using looping
3.Write a program toprint sum of 10 numbers;
4.Write a program to print the maximum of n numbers;
5.Write a program to operate switch case statement
6.Write a program to find out the prime numbers among 1 to user choice(n)
7.Write a program to find out the leap years from 1900 to today’s date
8.Write a program to count vowels in a given strings.
9.Write a program to check given strings are equal or not .
10.Write a program to input weekday number and print the weekday
11.Write a program to design a simple calculator using if else if statements
12.Write a program to design a simple calculator using switch case statement
case 1: Addition’
case 2 : Subtraction
case 3 : Multiplication
case 4 ; Division
default: print “wrong choice”
Sample example :
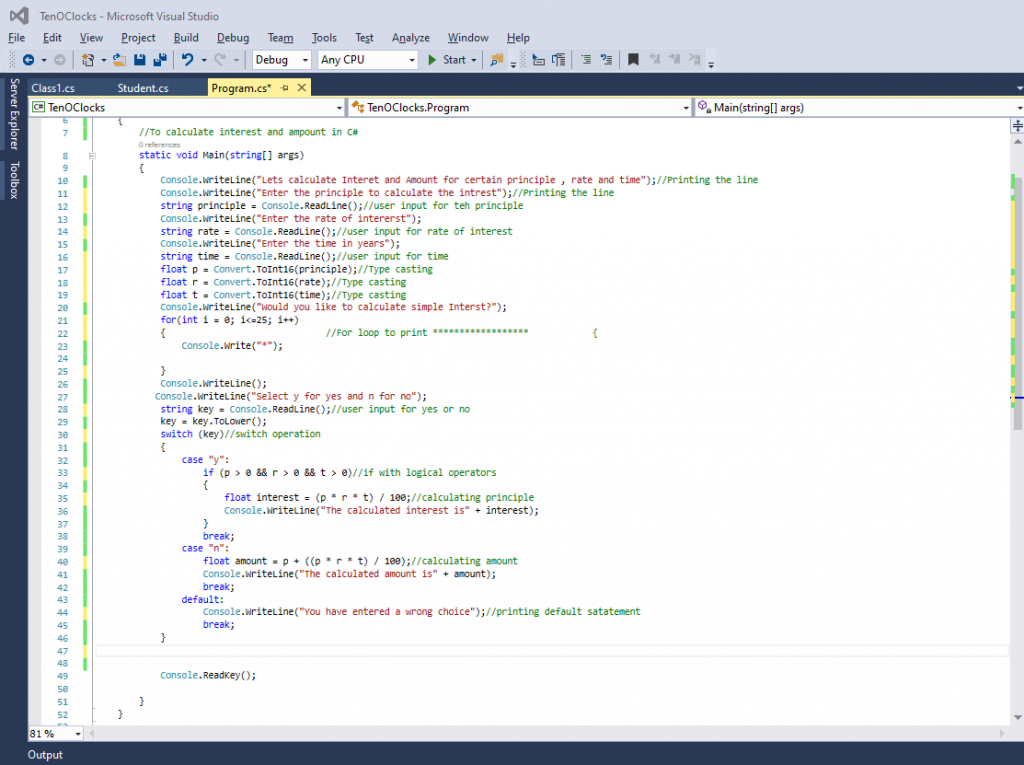
namespace TenOClocks
{
public class Program
{
//To calculate interest and ampount in C#
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("Lets calculate Interet and Amount for certain principle , rate and time");//Printing the line
Console.WriteLine("Enter the principle to calculate the intrest");//Printing the line
string principle = Console.ReadLine();//user input for teh principle
Console.WriteLine("Enter the rate of intererst");
string rate = Console.ReadLine();//user input for rate of interest
Console.WriteLine("Enter the time in years");
string time = Console.ReadLine();//user input for time
float p = Convert.ToInt16(principle);//Type casting
float r = Convert.ToInt16(rate);//Type casting
float t = Convert.ToInt16(time);//Type casting
Console.WriteLine("Would you like to calculate simple Interst?");
for(int i = 0; i<=25; i++)
{ //For loop to print **** {
Console.Write("*");
}
Console.WriteLine();
Console.WriteLine("Select y for yes and n for no");
string key = Console.ReadLine();//user input for yes or no
key = key.ToLower();
switch (key)//switch operation
{
case "y":
if (p > 0 && r > 0 && t > 0)//if with logical operators
{
float interest = (p * r * t) / 100;//calculating principle
Console.WriteLine("The calculated interest is" + interest);
}
break;
case "n":
float amount = p + ((p * r * t) / 100);//calculating amount
Console.WriteLine("The calculated amount is" + amount);
break;
default:
Console.WriteLine("You have entered a wrong choice");//printing default satatement
break;
}
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
output:
Lets calculate Interet and Amount for certain principle , rate and time
Enter the principle to calculate the intrest
1000
Enter the rate of intererst
10
Enter the time in years
2
Would you like to calculate simple Interst?
Select y for yes and n for no
y
The calculated interest is200
** This is the end of the starting phase.You are ready to move on for the beginner phase where we will concentrate towards below topics.
- Some more data types
- Boxing and unboxing
- Strings, Arrays
- Standard loopings
- Standard conditional statements
- Functions
- Simple Class and Object
