Here, we will learn about the Conditional Statements in C#.
A statement that can be executed based on a condition is known as a “Conditional Statement”.
Less than: a < b
Less than or equal to a <= b
Greater than: a > b
Greater than or equal to a >= b
Equal to a == b
Not Equal to: a != b
You can use these conditions to perform different actions for different decisions.
We have different conditional statements in c# to handle all the operations:
if and nested if statement
switch and nested switch statement
if-else and nested if-else Statement
** We also use ternary and Lambda expressions to make the code more effective.
if Statement:
Use the if statement to specify a block of C# code to be executed if a condition is True. C# is case sensitive so writing uppercase letters (If or IF) will generate an error.
else Statement:
Use the else statement to specify a block of code to be executed if the condition is False.
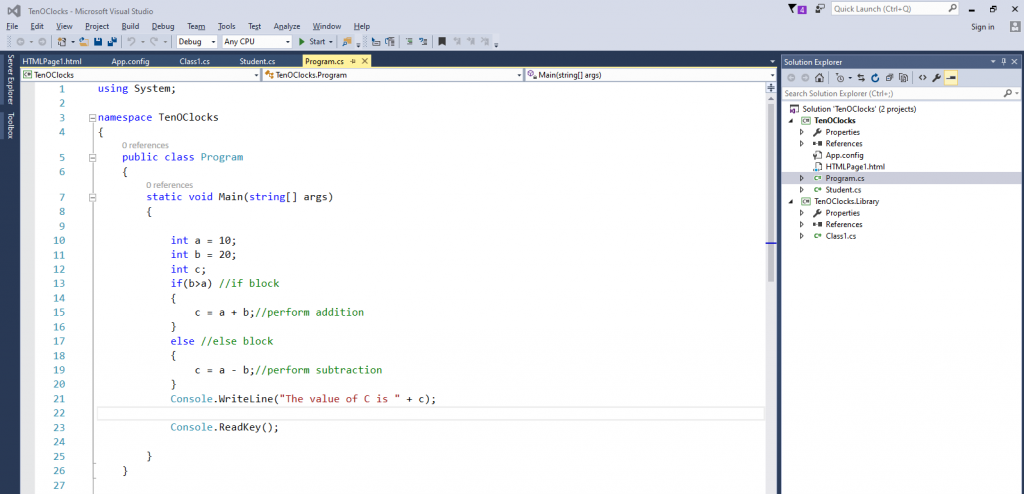
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int a = 10;
int b = 20;
int c;
if(b>a) //if block
{
c = a + b;//performs addition
}
else //else block
{
c = a - b;//performs substraction
}
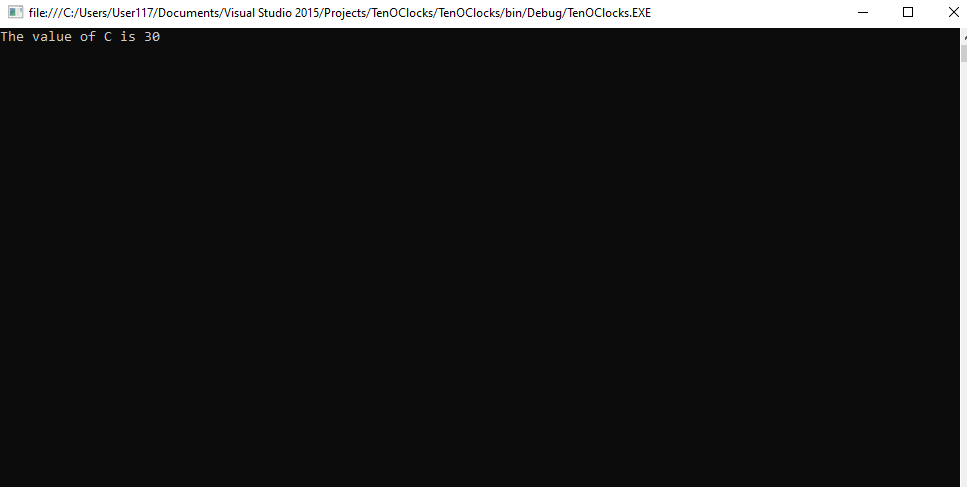
Console.WriteLine("The value of C is " + c);
Console.ReadKey();
}Nested if:
If within if statement is nested if
if(condition)
{
statement
if(condition)
{
statement
statement
}
}Nested if-else:
If else within if or else statement is Nested if-else.
if(condition)
{
//statement
if(condition)
{
//statement
//statement
}
else
{
//statement
}
}If -else-if :
if(condition)
{
//statement
}
else if(condition)
{
//statement
//statement
}
else
{
//statement
}
Sample example illustrating all if operations:
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int a = 10;
int b = 20;
int c;
#region if operation
if (a > b && a != 15)// if with and operators
{
a += b;
a--;
Console.WriteLine(++a);
}
#endregion
#region nested if operation
if (a > 10)// if condition
{
a += b; //a= a +b;
a--; //unary operator
if (a > 25)
{
Console.WriteLine(++a);//printing the incremented value of a
}
}
#endregion
#region if-else operation
if (a > 10)// if condition
{
a += b; //a= a +b;
a--; //unary operator
Console.WriteLine(++a);//printing the incremented value of a
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine(++b);//printing the incremented value of b
}
#endregion
#region nested if-else operation
if (a > 10)// if condition
{
a += b; //a= a +b;
a--; //unary operator
if (a != 5)
{
Console.WriteLine("a not equal to 5");//printing
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("a equal to 5");//printing
}
Console.WriteLine(++a);//printing the incremented value of a
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine(++b);//printing the incremented value of b
}
#endregion
#region if else-if else
if (a > 5)
{
Console.WriteLine(++a);//printing the incremented value of a
}
else if (a < b)
{
Console.WriteLine(++a);//printing the incremented value of a
}
else
{
c = a * b;
Console.WriteLine(c);//printing the incremented value of c
}
#endregion
Console.ReadKey();
}
In the above sample, we can see nested if -else, so whenever we talk about if-else then if the condition in if is false then else gets executed.
If you have one statement for any conditional statement you can avoid braces (interpolation):
You can write
if(a >b)
Console.WriteLine(b);//printing the incremented value of b
else
Console.WriteLine(a);//printing the incremented value of a
**Switch Case operations will be seen in the next article.
